17+ Years, More than 25000 clients and 10000+
company registrations done
Overview
An organization that is set up with two or more individuals to run a business in order to make a profit, is called a Partnership Firm. Each member of such a group is recognized as a partner and is known collectively as a partnership firm.
The Indian Partnership Act, 1932 discusses issues that regulate partnerships. A crucial feature of the partnership is that each partner is both a principal and an agent for all the other partners of the firm, so an act of one partner is an act of all partners. In simpler words, this means that each partner is responsible for the actions of other partners of the firm (unlimited liability).
Registration of a Partnership Firm is not compulsory in India, but it is recommended that one registers a Partnership firm considering the advantages of a registered company and limitations on access to a court of law for the enforcement of a partner’s rights.
What Is The Process?
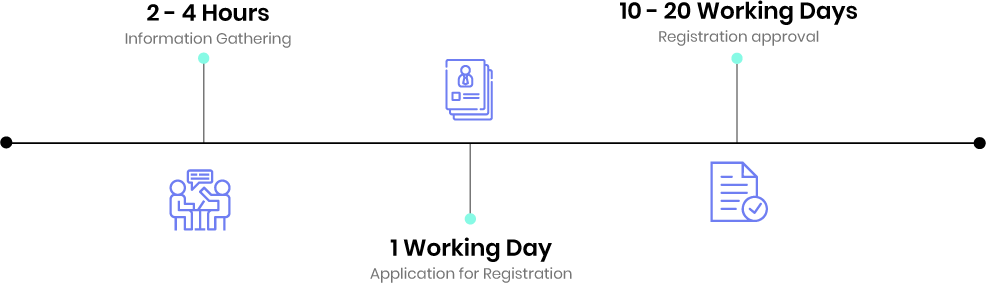
- A Partnership Firm is registered by the Registrar of Firm of the Indian State where the office of the firm is located. The procedure and requirements for registration of Partnership Firm is fairly straight forward.
- Application for Registration of Partnership Firm has to be made (Form 1 of the State Registrar of Firm).
Details Required
- Partnership Deed
- PAN card of Partners
- Address Proof of Partners
- Address Proof of the Firm or Rental Agreement of the place
- NOC from the landowner
Timeline
Testimonials
Get Started
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Should a Partnership Firm be registered?
Under the Partnership Act of 1932, there is no such clause, which mandates the registration of a partnership. The Act itself, however, provides for the process for the firm’s registration. Registration is therefore voluntary but strongly recommended, as any amount in excess of INR 100/- cannot be recovered by an unregistered firm. In addition to the above legal impediment, the firm should also be registered from a practical point of view in order to provide clarity in the relationship between partners and the firm per se.
2. Is a written partnership deed necessary to form a Partnership Firm?
No, it’s not required. As per the contract act, it is not mandatory to provide a written agreement. It is always advisable, however, to create a partnership deed, in order to provide it to the bank, income tax authorities, and customers with whom the partnership firm deals. A written partnership deed, apart from acting as a reference document, often helps in reducing disputes and uncertainty over time.
3. Is it necessary to draft a Partnership Deed?
A written partnership deed is not mandatory. However, it is advisable, as a written partnership deed, apart from acting as a reference document, often helps in reducing disputes and uncertainty over time.
4. What is the personal liability of the partner for the business obligations of the Partnership Firm?
In the case of Business obligations of a partnership, all partners are personally liable. This implies that the partners are collectively liable for paying the debts if the firm cannot afford to pay creditors or in case the business fails, and creditors can go after personal assets such as bank accounts, vehicles, and even partners’ houses. For example, if the partnership dissolves and debts to suppliers or lenders are still unpaid, such creditors can sue the partners individually to pay for the debts. Unless it is a limited partner, the partnership’s debts will expose personal assets to liability. In the case of Limited Partner, liability is limited to the money invested.
5. What is a dissolution of a partnership firm?
As per Section 39 of the Indian Partnership Act, “the dissolution of the partnership between all the partners of a firm is referred to as the dissolution of a firm.” This means that the partnership arrangement between all the partners is fully broken down.
6. What is the rate of income tax on partnership firm?
At 30% of the total income, a partnership firm needs to pay income tax. If the overall income crosses 1 crore, then at the rate of 12%, a partnership company must pay the income tax surcharge on the amount of income tax. A partnership firm must pay education cess and a second higher education cess in addition to the income tax and surcharge. Education Cess is applicable at the rate of 2 % on the amount of income tax and the applicable surcharge. Cess in secondary and higher education is applicable at the rate of 1 % on the amount of income tax and the applicable surcharge.
7. Can a minor admitted to the benefits of partnership, become a partner on attaining a majority?
Within six months of reaching the majority, a minor admitted to the benefits of partnership has the option of becoming a partner. He must offer a public notice stating his approval of the partnership or rejection of it. It is deemed that he has been a partner of the company in the absence of a note.
8. What are its implications of a partner being served a notice?
A notice served on any of the partners who handle the firm’s affairs is considered, under the law, as a notice on the entire organization. However, it shall not be treated as a notice to the firm in the event of fraud committed on the firm by or with the consent of the managing partner, but as a notice only to that partner who has committed fraud.
9. Can a partner transfer his right in the business of the firm to an outsider?
Yes, a partner, but only with the agreement of all other partners, can pass his interest in the business to an outsider.
10. Can a new partner be admitted into the Partnership Firm?
A partner may appoint a successor to take his position in the event of the partner’s death or retirement. The manner in which a new partner or successor is introduced is dependent on clauses in the partnership deed. If the new partner is accepted into the company, a new partnership deed is required.
11. Can a Hindu Undivided Family become a partner of a firm?
The status of a HUF is not that of a legal person and therefore, it cannot enter into a partnership with either an individual or another HUF.























