17+ Years, More than 25000 clients and 3000+
company registrations done
Overview
Certain provisions under the Indian Income Tax Act of 1961 exempt income received by certain entities or activities. An entity that gets registered under Section 12A of the Income Tax Act of 1961 is exempted from paying income taxes.
The exemption is available to:
- Income received by any person on behalf of the university, or other educational institution or any hospital.
- Income derived from property held under trust wholly for charitable or religious purposes.
It is mandatory for an entity to get registration under Section 12A of the Income-tax Act, 1961 so as to claim exemption. Furthermore, donors or contributors to an entity can claim exemption from Income Tax if the entity has obtained certification under section 80G of the Income Tax Act. Application for registration under both section 12A and 80G can be applied just after registration/ establishment of the entity. However, for registration under section 80G, prior registration under section 12A is required.
What Is The Process?
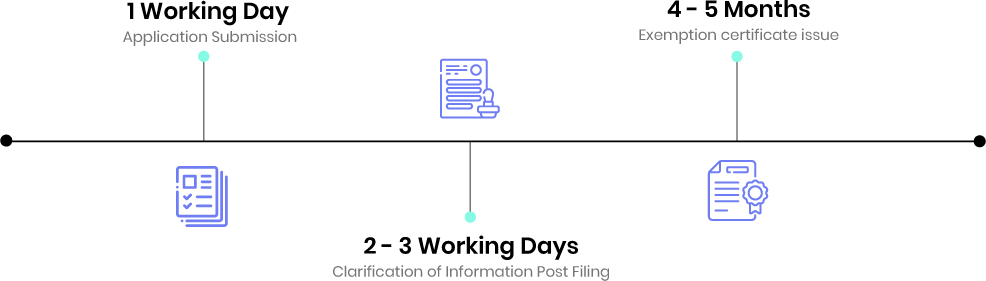
Application submission
The application is submitted with relevant information under the appropriate jurisdiction of the Income Tax Department.
Post filing clarifications
Income Tax Department will ask for clarification post-filing of the application.
Representation and response
An applicant or its authorized representative will have to respond to the clarifications sought and furnish other information/ documents asked for. Sometimes, personal hearing is required to clarify the objections.
Issuing of certificate
Finally, the Exemption Certificate is issued.
Details Required
- Duly filled Form.
- Permanent Account Number (PAN)
- Self-certified copy of instrument showing incorporation or registration of the entity
- Documents governing the conduct of the entity (MoA, Trust Deed).
- List and details of Governing Body, Board of Trustees, etc.
- Residential proof with less than two months old utility bill
- NOC from the landlord of the land/ premises
- Books of Accounts, Balance Sheet, and Income Tax Return (ITR) for the last three years or since inception
- Information about welfare activities carried out
- Progress Report for the last three years or since inception
- List of contributors along with their PAN and Address
- Details of shares, security, or property purchased by the entity
- Any income from property conferring benefit
Timeline
Testimonials
Get Started
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can both the applications under section 12A and 80G of the Income Tax Act be applied together?
Yes, both applications under section 12A and 80G of the Income Tax Act can be applied together or it can also be applied separately. If some organization is willing to apply separately, an application for registration under section 12A will be applied first. It is pertinent to get registration under 12A for the registration under 80G of the Income Tax Act.
2. How is “income” defined in case of a charitable trust or institution?
In the case of a charitable trust or institution, “Income”, has to be understood in the broadest of terms. such income under this will include income falling under different heads of income, including profits and gains of business or profession, capital gains, income from house property, and income from other sources (such as dividends, interest on securities, etc.) as it is in the case of any other assessee. Additionally, in the case of a charitable trust or institution, donations received (“voluntary contributions”), which otherwise do not possess the character of “income” are also to be included in income. All these amounts will, in the first instance, be included in the income of the charitable trust or institution, and, thereafter, the exemption can be claimed subject to fulfillment of prescribed conditions.
3. When is registration ordinarily refused by the CIT (Commission of Income Tax)?
The CIT will ordinarily refuse registration if:
- Trust is not a public charitable/religious trust
- Objects of the trust are not charitable
- Some matter exists only for the benefiting the settler or trustees or their relatives thereof,
- A provision exists for the transfer of any part of the income or the assets of the trust to any private individual or body.
- The trust is created for the benefit of any specific religious community or caste or individual and not for the public at large.
4. What is the difference between 12A and 80G?
Under Sec 12A, NGO can avail income tax exemption by getting itself registered and complying with certain other formalities and Under Sec 80G, Donee will get the benefit of tax exemption of amount given as a donation.
5. How do I register a trust under section 12A?
Trust can be registered under the Income Tax Act under sec. 12A by applying online on the Income Tax website.
6. When can an organization apply for registration under section 12A and 80G of the Income Tax Act?
Application for registration under section 12A and 80G can be applied just after registration of the NGO.
7. Where should the application be made under section 12A and 80G of the Income Tax Act?
Application for registration under section 12A and 80G can be made to the Commissioner of Income Tax (Exemption) having jurisdiction over the institution.























