EPO’s Fourth Industrial Revolution: Examining Changing Trends
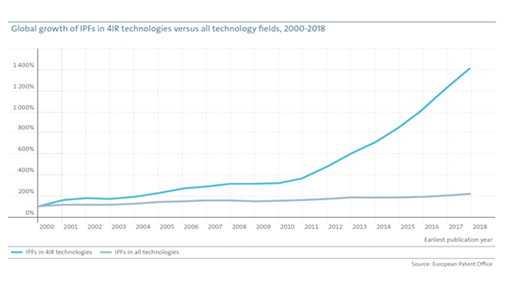
The European Patent Office released its study titled “Patents and the Fourth Industrial Revolution – the Global technology trends enabling the data-driven economy” in December 2020. The study revealed that innovation in the fourth industrial revolution (4IR) has accelerated worldwide. This study primarily revolves around the International Patent families related to 4IR worldwide between 2000 and 2018. It said that between 2010 and 2018, global patent filings for these technologies, which concern smart connected objects and span the Internet of Things, big data, 5G, and artificial intelligence (AI), grew at an average annual rate of almost 20% – nearly five times faster than the average of all technology fields.
[Image Source: The Economic Transcript]
This mainly represented a high-value invention for which a patent application has been filed in two or more patent offices globally. Interestingly, the study revealed that more than 40000 of the application, which accounts for more than 10% of the patenting activity worldwide, for the 4IR technology, were filed in 2018 alone. What 4IR denotes is the full integration of information and communication technologies (ICT) in the context of manufacturing and application areas such as personal, home, vehicle, enterprise, and infrastructure, marking a radical step towards a fully data-driven economy. By 2023, the study estimates, more than 29 billion devices will be connected to Internet Protocol networks across the globe, most of which will be creating data in real-time.
The Technologies
4IR has been divided into three main sectors: core technologies, enabling technologies, and the application domain. These 4IR inventions were grouped into one or more of these three main types. What these three sectors constitute? Core technology comprises those which make it possible to transform any object into a smart and connected device, namely three fields as connectivity, IT hardware, and software. Enabling technologies are used in combination with connected objects. This study comprises eight fields: data management, user interfaces, geo-positioning, data security, safety, 3D systems, power supply, and core AI. While the application domains are those where the potential of connected objects can be exploited, there are eight domains: consumer goods, services, vehicles, healthcare, industrial, home, infrastructure, and agriculture. Therefore, the core technologies are basic building blocks upon which the technologies of 4IR are built. While the enabling technologies complement the core technologies and finally the application domain puts the technology in various parts of the domain.
The Finding
4IR innovation is accelerating strongly. The average annual growth rate was 12.8% from 2000 to 2009, increasing close to 20% from 2010 to 2018. Since 2010, the number of IPFs has grown at a rate of 23.0% in core technologies, 20.3% in enabling technologies, and 19.0% in application domains.
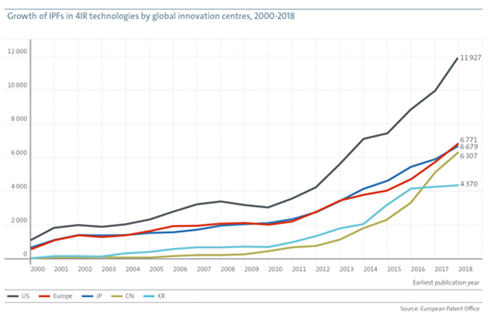
The US was the most innovative world region among all the applicants in the 4IR technology having its presence in all the sectors, outpacing Europe and Japan, each account for about one-fifth of all IPFs in 4IR since 2000. Korea and China accounted for 10% of all IPF and with faster growth.
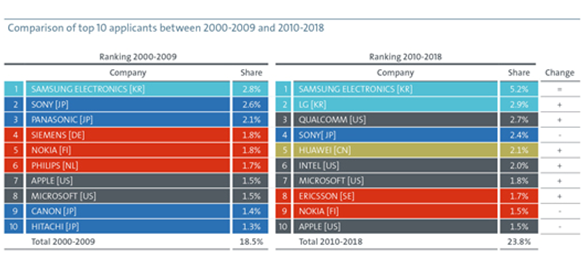
The study analyzed the work of various applicants where 25 of all applicants together accounted for more than 37.9% of all IPF. As compared with all the applicants, Japan had the most number of companies (9) followed by the US (7) and Europe (5), whereby Samsung was the clear leader with a 5.2% share. Despite more Japanese companies’ innovation in 4IR technologies was largely dominated by the US (32%), Europe (20%), and Japan (19%), which together accounted for more than 70% of all IPFs.
Graph Source- https://www.epo.org/news-events/in-focus/ict/fourth-industrial-revolution.html
In exchange for limited exclusive rights, all patent applications are published, revealing the inventions’ technical details. Patent databases, therefore, contain the latest technical information, much of which cannot be found in any other source, which anyone can use for their research purposes. The EPO’s free Espacenet database contains more than 120 million documents from over 100 countries and comes with a machine translation tool in 32 languages. This patent information provides early indications of the technological developments that are bound to transform the economy. It reveals how innovation is driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution. (www.epo.org)
Author: Saransh Chaturvedi (an advocate) currently pursuing LLM from Rajiv Gandhi School of Intellectual Property Law (IIT Kharagpur). In case of any queries please contact/write back to us at support@ipandlegalfilings.com.